
Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene and conserved protein-coding markers revealed that strain RT761 was assigned to the clade OP9 of “ Ca. Atribacteria”.Ī bacterium, designated RT761, was isolated after 3 years of enrichment from saline formation water and sediments derived from deep aquifers in natural-gas deposits in Japan.
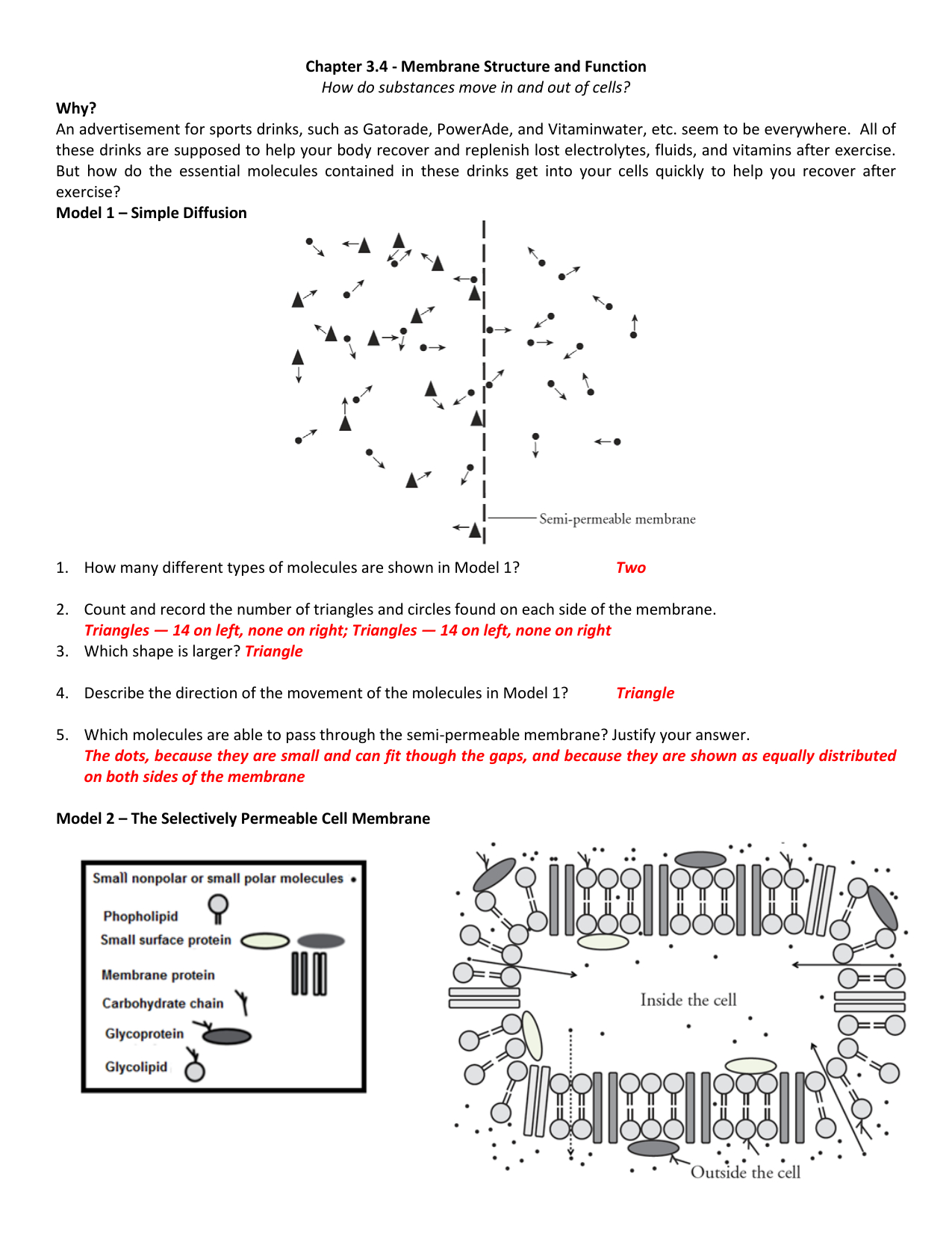
Here, we report structural, genomic and physiological characterization of the cultured representative of “ Ca. The members of this phylum are globally distributed and, in some cases abundant, in anaerobic environments 5. Atribacteria” was originally discovered through 16S rRNA gene clones in sediments from the hot spring in Yellowstone National Park and designated as OP9 in 1998 8, and recently proposed to include the JS1 lineage 5. Caldatribacteriota” in Genome Taxonomy Database 7). In this study, we have isolated an anaerobic bacterium that belongs to the bacterial candidate phylum “ Ca. While omics-based cultivation-independent characterization can circumvent cultivation and provide insight into metabolism and ecology 4, 5, metabolic reconstruction is generally based on genes characterized in cultured organisms and, thus, prediction of novel phenotypic features of uncultured microorganisms remains challenging 6. However, most lineages of the domains Bacteria and Archaea remain uncharacterized 1 due to difficulties in cultivation 2, 3.

nov.Ĭultivation of uncultured microorganisms is a critical step in uncovering their phenotypic features, such as cell structure and metabolic function. We propose RT761 as a new species, Atribacter laminatus gen. Physiologically, RT761 primarily produces hydrogen for electron disposal during sugar degradation, and co-cultivation with a hydrogen-scavenging methanogen improves growth.
/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png)
The RT761 genome encodes proteins with features that might be related to the complex cellular structure, including: N-terminal extensions in proteins involved in important processes (such as cell-division protein FtsZ) one of the highest percentages of transmembrane proteins among gram-negative bacteria and predicted Sec-secreted proteins with unique signal peptides. However, further studies are needed to provide conclusive evidence for this unique intracellular structure. Our observations are consistent with a classical gram-negative structure with an additional intracytoplasmic membrane. The isolate, RT761, is a subsurface-derived anaerobic bacterium that appears to have three lipid membrane-like layers, as shown by cryo-electron tomography. Here, we isolate a member of the ubiquitous, yet-to-be-cultivated phylum ‘ Candidatus Atribacteria’ (also known as OP9) that has an intracytoplasmic membrane apparently surrounding the nucleoid. A key feature that differentiates prokaryotic cells from eukaryotes is the absence of an intracellular membrane surrounding the chromosomal DNA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
